Measuring Progress with Percentages in JavaScript: A Practical Guide

When building applications that track user progress—such as to-do lists, learning platforms, or project management dashboards—you’ll often need to calculate the percentage of tasks completed. This percentage provides a clear, user-friendly way to communicate progress at a glance.
Let’s break down the logic, explore how to implement it in JavaScript, and cover important considerations along the way.
1. Understanding the Basic Formula
At its core, calculating progress is straightforward. You only need:
- Total items (how many tasks exist overall)
- Completed items (how many tasks are marked as done)
The formula looks like this:
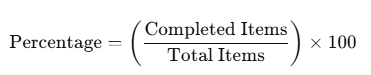
For example, if there are 41 tasks in total and 10 are completed:
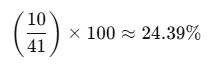
So the progress percentage is 24.39%.
2. Implementing in JavaScript
Here’s a simple example in plain JavaScript:
const totalItems = 41;
const completedItems = 10;
const percentage = (completedItems / totalItems) * 100;
console.log(percentage.toFixed(2) + "%"); // 24.39%
toFixed(2)ensures the number is formatted with two decimal places.- Without formatting, you might end up with long decimals like
24.390243902439025.
3. Working with Arrays of Objects
In real-world applications, progress items are often stored as an array of objects, each with a property like is_completed. For example:
const progressItems = [
{ id: 1, is_completed: true },
{ id: 2, is_completed: false },
{ id: 3, is_completed: true },
// ... more items
];
You can calculate progress dynamically:
const totalItems = progressItems.length;
const completedItems = progressItems.filter(item => item.is_completed).length;
const percentage = (completedItems / totalItems) * 100;
console.log(`Progress: ${percentage.toFixed(2)}%`);
This way, no matter how many items are in the array, the calculation stays accurate.
4. Important Considerations
While the formula is simple, there are edge cases and design decisions you should keep in mind:
✅ Handling Zero Items
If totalItems = 0, dividing by zero will break the calculation. Always check first:
const percentage = totalItems > 0
? (completedItems / totalItems) * 100
: 0;
This ensures your app doesn’t show NaN% or throw errors.
✅ Rounding vs. Precision
- Rounding up (ceil) can make progress feel more encouraging to users.
- Rounding down (floor) can be more conservative.
- Two decimals is usually a good balance for readability.
✅ Display Format
You don’t always need decimals. For user interfaces, whole numbers often look cleaner:
Math.round(percentage) + "%";
Example: instead of 24.39%, you may just show 24%.
✅ Visual Feedback
Percentages are often paired with progress bars or circular indicators for a more engaging UI.
Example with CSS progress bar:
<div style="background:#eee; width:200px; height:20px; border-radius:5px;">
<div style="background:#4caf50; width:24%; height:100%; border-radius:5px;"></div>
</div>
5. Real-World Use Cases
- E-learning apps: showing how much of a course is complete.
- Fitness trackers: calculating workout progress.
- Project management tools: visualizing tasks completed.
- Gamification: giving users a sense of achievement when they see progress grow.
6. Finally
Calculating progress in JavaScript is not just about numbers—it’s about giving users a clear sense of achievement. By using a simple formula, formatting results correctly, and handling edge cases like zero items, you can provide a robust and user-friendly solution.
Key takeaways:
- Always divide completed / total × 100.
- Format results for readability (
toFixed,Math.round, etc.). - Handle zero cases to avoid errors.
- Consider user experience when displaying percentages.
With these principles in place, you can transform raw numbers into meaningful progress indicators that keep users engaged and motivated.



Comments ()